Audi Q7: A/C System Operation
General Information
The temperature in the passenger compartment depends on the amount of heat radiated through the windows and conducted by the metal parts of the body. In hot weather it is possible to achieve a more comfortable temperature for the passengers by pumping off some of the heat.
As heat spreads into cooler areas, the passenger compartment is equipped with a unit for generating low temperatures. In the unit, refrigerant is constantly evaporated. The heat required for this is extracted from the air flowing through the evaporator.
After absorbing heat, the refrigerant is pumped off through the compressor. The action of the A/C compressor increases the heat content and temperature of the refrigerant. Its temperature is then substantially higher than that of the surrounding air.
The warm refrigerant flows to the condenser. There, the refrigerant dissipates its heat through the condenser to the surrounding air due to the temperature difference between the refrigerant and air.
The refrigerant thus acts as a heat transfer medium. As it is to be reused, the refrigerant is returned to the evaporator.
For this reason all air conditioning systems are based on the refrigerant circulation principle. There are however differences in the combination of aggregates.
Comfort
Being comfortable while driving leads to better concentration and safe driving. Air conditioning makes drivers and passengers more comfortable when temperatures or humidity are high. While opening the windows or sunroof or increasing the air flow can make vehicle occupants more comfortable, it also exposes them to more noise, draughts, exhaust, pollen and dust.
A well-designed heating and air conditioning system can increase comfort by controlling the temperature, humidity and air flow inside the vehicle. This is done both when the vehicle is moving and when it is stationary.
Air conditioning also offers these advantages:
- It cleans the air that enters the vehicle interior. The damp fins on the evaporator collect dust and pollen, which is then removed by condensation.
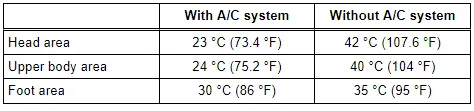
- Temperatures in a mid-size vehicle (for example: after a short drive, outside temperature 30 ºC (86 ºF) in the shade and the vehicle exposed to sunlight).
Environmental Information
Since roughly 1992, the air conditioning systems of newly manufactured cars have been successively converted to refrigerant R134a. This refrigerant does not contain chlorine and does not deplete the ozone layer.
Until roughly 1992, refrigerant R12 was used for air conditioning systems. Due to its chlorine atoms, this CFC has a high potential for depleting the ozone layer as well as a tendency to increase the greenhouse effect.
Conversion programs are available for old existing systems filled with the ozone-depleting substance R12. Refer to Repair Manual for A/C Systems with Refrigerant R12 (this repair manual is only available in hard copy).
The greenhouse potential of R134a (Global Warming Potential = GWP) is approximately 1400, for this reason the European commission has committed that from 01/01/2017 no vehicles with this can newly be brought into the market. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant R134a Environmental Information". For this reason from 2016 for new vehicles a refrigerant with a GWP smaller than 150 in introduced (for example the refrigerant R1234yf with a GWP less than 5).
For environmental protection reasons, refrigerants must not be released into the atmosphere. For laws and regulations. Refer to → Chapter "Laws and Regulations".
General Safety Precautions
- As per VBG 20, German industrial liability insurance association.
- Pay attention to the workshop-specific instructions. It should be kept in the workshop.
Product Characteristics
Refrigerants used in motor vehicle air conditioning systems belong to the new generation of refrigerants based on chlorine-free, partially fluorinated hydrocarbons (H-FKW, R134a).
With regard to their physical properties, these are refrigerants which have been liquefied under pressure. They are subject to the regulations governing pressure containers and use is only to be made of approved and appropriately marked containers.
Compliance with specific conditions is required to ensure safe and proper use.
Handling Refrigerant
If refrigerant containers are opened, the contents may escape in liquid or vapor form. This process is intensified the higher the pressure in the container.
The pressure level is governed by two factors:
- The type of refrigerant in the container. "The lower the boiling point, the higher the pressure."
- The temperature level. "The higher the temperature, the higher the pressure."
 WARNING
WARNING
- There is a danger of ice-up.
- The refrigerant can then escape as a fluid or vapor.
- Do not open containers which store refrigerant.
Protective Eyewear
Put on protective goggles. They prevent refrigerant getting into the eyes, as this could cause severe injury from exposure to cold.
Protective Gloves and Clothing
Greases and oils dissolve readily in refrigerants. They would therefore destroy the protective layer of grease if allowed to come into contact with the skin. Degreased skin is however sensitive to the cold and germs.
Fluid Refrigerant and Skin Precaution
The refrigerant draws heat for evaporation from the surrounding area. Even if this is the skin. This may cause extremely low temperatures. Local frost bite may result (boiling point of R134a: -26.5 ºC (-15.7 ºF) at ambient pressure).
Refrigerant Vapor Precaution
If highly concentrated refrigerant vapor escapes, it mixes with the surrounding air and displaces the oxygen necessary for breathing.
Welding and Soldering on Refrigeration Systems
Before performing welding or soldering work on vehicles near A/C system components, extract the refrigerant and remove remnants by blowing them out with nitrogen.
The products of refrigerant decomposition due to the effect of heat are not only toxic, but may also have a highly corrosive effect on pipes and system components. They mainly take the form of hydrogen fluoride.
Pungent Odor
A pungent odor indicates that the products of decomposition mentioned above have already formed. Avoid inhaling these substances under all circumstances, as otherwise the respiratory system, lungs and other organs could be damaged.
First Aid
- Following contact with eyes or mucous membranes, immediately rinse with copious amounts of running water and consult an eye specialist.
- Following contact with the skin, immediately remove affected clothing and rinse skin with copious amounts of water.
- Following inhalation of highly concentrated refrigerant vapors, immediately take the affected person into the open air. Call a doctor. Administer oxygen in the event of breathing difficulties. If the affected person has difficulty breathing or cannot breathe, tip head back and perform mouth to mouth respiration.
Handling Pressure Containers
Secure containers to prevent them falling over!
Secure upright cylinders to stop them falling over and cylinders lying flat to stop them rolling away.
Do not throw containers!
If dropped, the containers could be so severely deformed that they rupture. The refrigerant evaporates immediately, liberating considerable force. Flying fragments of cylinders can cause severe injuries.
To protect the valves, cylinders are only to be transported with protective cap screwed on.
Valves may break off if cylinders are not properly transported.
Never store in the vicinity of radiators.
High temperatures may occur next to radiators. High temperatures are also accompanied by high pressures and the maximum permissible container pressure may be exceeded.
Not Warming Above 50 ºC (122 ºF)
To avoid possible risk, pressure container regulations specify that containers are not to be heated to in excess of 50 ºC (122 ºF).
Heating Warning
Do not heat with a naked flame under any circumstances. Localized overheating can cause structural changes in the container material, which then reduce its ability to withstand pressure. There is also a danger of refrigerant decomposition due to localized overheating.
Empty Containers
Empty refrigerant containers must always be sealed to prevent the ingress of moisture. Moisture causes steel containers to corrode. This weakens the containers walls. In addition, rust particles entering into refrigeration systems from containers will cause malfunctioning.
Extraction and Charging System Safety Regulations
- Make sure the shut-off valves are closed before connecting the charging system to the air conditioning system.
- Before disconnecting the charging system from the air conditioning system, make sure the charging process has been completed to stop refrigerant escaping into the atmosphere.
- Once the purified refrigerant from the charging system has been transferred to an external compressed-gas cylinder, close the hand shut-off valves at the cylinder and charging system.
- Do not expose charging system to moisture or use it in a wet environment.
- Disconnect from power supply before performing service work on the charging system.
- Never use an extension cable on account of the fire hazard. If the use of an extension cable is unavoidable, the minimum cross-section should be 2.5 mm2.
- In case of fire, remove the external cylinder.
- Entrained oil from the air conditioning system drawn by the suction unit into the measurement container supplied is subsequently to be transferred to a sealed container as it contains a small quantity of refrigerant. It must not be released into the environment.
- Following shutdown, the service station is to be secured to stop it rolling away.
A/C System and Refrigerant R134a Safety Precautions
Vehicles with a high-voltage system (hybrid vehicles)
Extremely Dangerous Due to High-Voltage
The high-voltage system is under high-voltage. Electrocution can cause death or very serious personal injury from damages high-voltage components and high-voltage cables.
- Perform a visual inspection of the high-voltage components and the high-voltage cables.
- Never use tools that are for cutting, deformed, or sharp edged.
- Never use welding, soldering, thermal adhesive or hot air.
There is a Risk of Injury from the Engine Starting Unexpectedly
On electric - hybrid vehicles an active ready mode is difficult to identify. Parts of the body can be clamped or pulled.
- Turn off the ignition.
- Place the ignition key outside of the vehicle interior.
Risk of Damaging the High-Voltage Cables
Misuse can damage the insulation of high-voltage cables or high-voltage connectors.
- Never support objects on the high-voltage cables and the high-voltage connectors.
- Never support tools on the high-voltage cables and the high-voltage connectors.
- Never sharply bend or kink the high-voltage cables.
- When connecting pay attention to the coding of the high-voltage connectors.
For all procedures on vehicles with high-voltage system pay attention to the additional warning message for these vehicles. Refer to → Chapter "Warnings when Working on Vehicles with High Voltage System".
Vehicles with Start/Stop System
There is a Risk of Injury from the Engine Starting Unexpectedly
The engine can start unexpectedly on vehicles with an activated Start/Stop System. A message appears in the instrument cluster indicating whether the Start/Stop System is activated.
- Deactivate the Start/Stop System: Turn off the ignition.
All Vehicles
 WARNING
WARNING
Asphyxiation, frostbite, and poisoning may occur as a result of leaking refrigerant
There is a risk of injury from leaking refrigerant
- Danger of asphyxiation from displacement of the surrounding air
- There is a risk of frostbite (or risk of freezer burn from the evaporating liquid refrigerant)
- There is a risk of poisoning from the byproducts
Corrective Action
- Work on the A/C system refrigerant circuit should only be performed in well ventilated areas.
- When handling refrigerant and working on the refrigerant circuit, make sure there is a good flow of oxygen (change the air at least one time each hour in the work area and three times per hour in enclosed spaces (for example, the work pit). Turn on the available workshop ventilation and exhaust systems.
- Only store containers and devices with refrigerant in well ventilated areas (not in basements or near basement staircases for example).
- Do not breathe in fumes from leaking refrigerant.
- When handling refrigerant and when working on the refrigerant circuit, wear suitable protective gloves and protective eyewear.
- It is recommended to have an eye-flushing bottle available.
- Work on the A/C system refrigerant circuit should only be performed in well ventilated areas. Switch on the available ventilation systems.
- Refrigerant must not be stored in low-lying areas such as basements or in their entry ways or windowsills.
First Aid Measures
- If the affected person has inhaled a high concentration of refrigerant vapors, immediately remove them from the contaminated area and bring and lay them in the fresh air. Keep the affected person warm and calm. Initiate artificial respiration if the affected person is experiencing troubled breathing and administer oxygen if necessary. If the affected person has difficulty breathing or cannot breathe, tip head back and perform mouth to mouth respiration. Consult a physician.
- Should liquid refrigerant come into contact with the eyes, rinse eyes thoroughly in water for approximately 15 minutes. Then apply eye drops and consult a doctor immediately, even if the eyes are not hurting.
- Never put anything in the mouth of an unconscious person. If the symptoms continue or if ever there is a concern, seek medical advice.
- The doctor must be informed that the injury was caused by refrigerant R134a. Should refrigerant come into contact with other parts of the body despite compliance with safety regulations, these must likewise be rinsed immediately for at least 15 minutes with cold or lukewarm water.
- If contact with eyes or mucous membranes occurs, immediately rinse with copious amounts of running water and consult an eye specialist.
- Immediately remove clothing that refrigerant has contacted and rinse the area of the skin affected with cold or lukewarm water. Do not use hot water. Seek medical attention if frostbite occurs.
 Note
Note
- The refrigerant has a faintly noticeable odor which is therefore not perceptible.
- The refrigerant is heavier than air and falls to lower lying areas such as the work pit, basements, and deep spots and displaces the breathable air and oxygen. Remaining in oxygen deprived areas is life endangering.
- Liquid refrigerant for example from a leak evaporates at an ambient pressure of approximately 1 bar at roughly -29 ºC (84 ºF). If the refrigerant evaporates on skin, it can cause cryogenic burning. Delicate organs for example the cornea, are especially at risk. Excessive frostbite may be life threatening.
- The refrigerant breaks down near flames or when it comes in contact with hot surfaces. There is a danger of becoming poisoned by the resulting toxic fumes if inhaled. A pungent odor indicates that the products of the decomposition mentioned above have already formed. Avoid inhaling these substances under all circumstances, as otherwise the respiratory system, lungs and other organs could be damaged.
- The specific dangers associated with the refrigerant, material data etc. can be found in the safety data sheets.
Never weld or hard/soft solder components of a filled A/C system. This also applies to welding and soldering on the vehicle, if there is a risk that it may heat up components in the A/C system. When performing paintwork repairs, the temperature in the drying booth or preheating zone must not exceed 80 ºC (176 ºF).
Reason:
Exposure to heat increases the pressure in the system, which could cause the pressure relief valve to open.
Corrective Measure:
- Discharge refrigerant circuit using A/C service station.
 Note
Note
Always replace damaged or leaking A/C system components. Do not attempt to repair them by welding or soldering.
Refrigerant reservoirs (for example, charging cylinders on the A/C service station) must never be subjected to excessive heat or exposed to direct sunlight.
Corrective Measure:
- Reservoirs must never be completely filled with liquid refrigerant. Without sufficient room for expansion (gas cushion), reservoirs will rupture with devastating effects in the event of a temperature increase. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant R134a Characteristics".
Refrigerant is never to be transferred to systems or vessels in which air is present.
Corrective Measure:
- Evacuate systems and reservoirs before charging with refrigerant.

